
Subarachnoid haemorrhage, which can increase the pressure in the veins in the retina, causing them to bleed.They do not always cause severe eye pain. Penetrating trauma can occur from high-velocity injuries such as grinding and hammering. Penetrating trauma - this will cause bleeding throughout the eye.Blunt trauma - suddenly compressing the eye - for example, if hit by a squash ball.Retinal macroaneurysms - swollen blood vessels on the retina, usually related to high blood pressure, atherosclerosis and smoking.Posterior vitreous detachment, often because it causes a retinal tear (see below).Normal blood vessels which are damaged.Damage to the back of the eye in very premature babies who have been on oxygen in special care baby units.Diabetic eye disease (the most common cause).Conditions in which this can occur include:

Abnormal blood vessels which grow because the back of the eye is short of oxygen.Trauma to the eye (the most common cause in younger people).Bleeding from tears in the retina caused by vitreous detachment (see below).Bleeding from abnormal new blood vessels forming in advanced diabetic eye disease.The most common causes, accounting for about 90% of all cases of vitreous haemorrhage, are: What are the causes of vitreous haemorrhage? The other common causes of vitreous haemorrhage also tend to occur in adults aged 60 and above, except for eye trauma, which can occur at any age. The most common cause of vitreous haemorrhage is severe diabetic eye disease, which is mainly seen in older adults. Who is likely to experience vitreous haemorrhage? This makes it one of the most common causes of sudden deterioration in vision. After that, infantile retinal hemorrhages are commonly associated with abusive head trauma however, they can occur with other conditions that cause increased intracranial pressure or intracranial hemorrhage, such as accidental trauma or asphyxiation, cerebral venous thrombosis, stroke, and encephalitis.Vitreous haemorrhage affects about 7 per 100,000 people each year. Practical Pointsīirth-related hemorrhages are typically gone by age 1 month. Severe hemorrhages can cause permanent visual loss. Retinal hemorrhages usually resolve on their own within weeks of diagnosis. Retinal hemorrhages can be seen on MR SWI imaging 2.

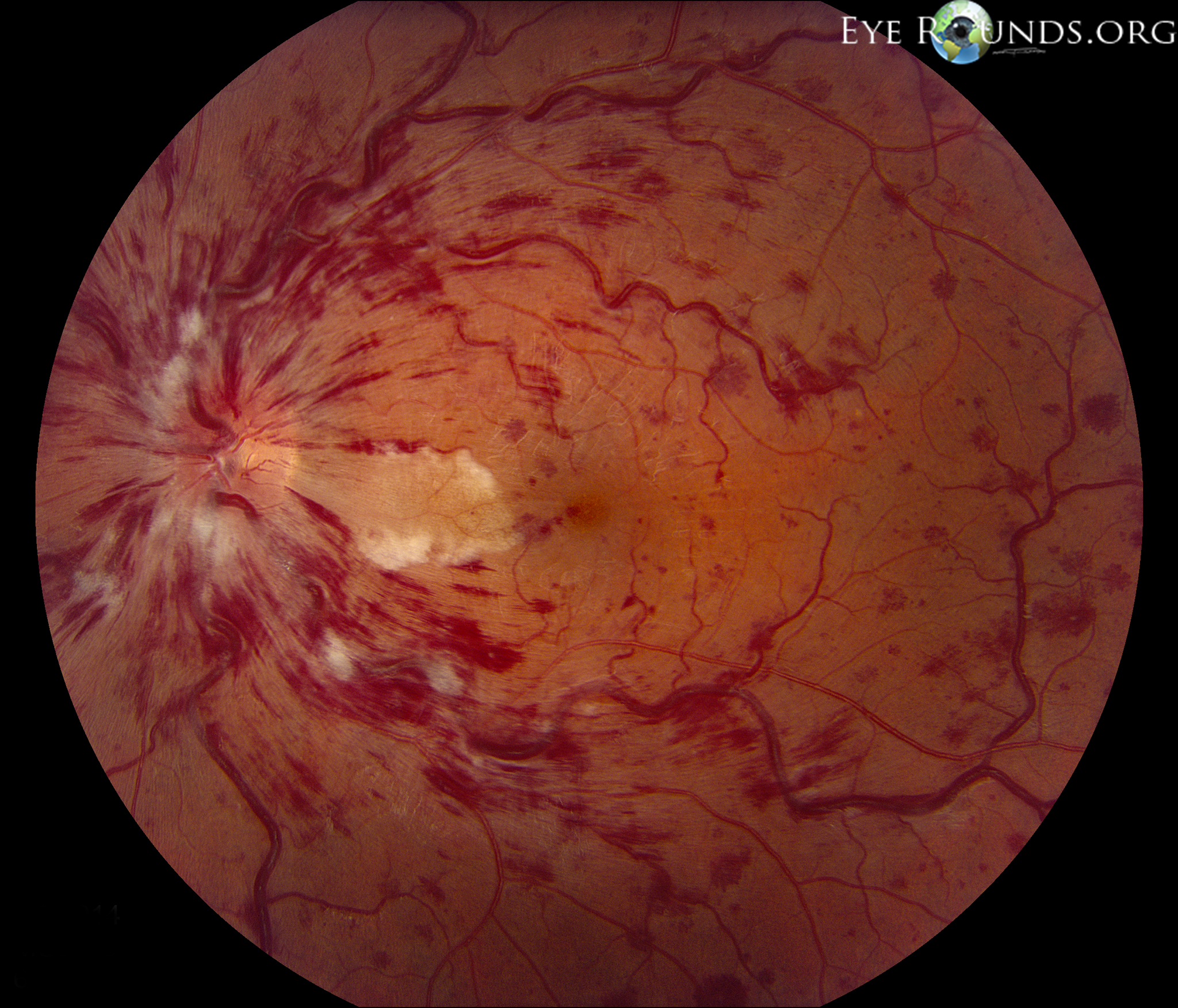
They have been described as dot/blot, boat-shaped, flame-shaped, or splinter-shaped. Retinal hemorrhages can appear to the ophthalmologist in various shapes depending on the layer(s) of the retina affected. Retinal hemorrhages are usually found in the setting of an acute infantile neurologic problem, such as seizure, lethargy, suspected or known head trauma. The only well-known incidence of infantile retinal hemorrhage comes from neonatal studies, where, in a recent study, 20% of full-term newborns were found to have retinal hemorrhages 1. Another common term used is 'fundus hemorrhage'. Retinal hemorrhages that are associated with intracranial hemorrhage, usually subarachnoid hemorrhage, are referred to as ' Terson syndrome', as described by Terson in 1900 (he actually described the association between vitreous hemorrhage and intracranial hemorrhage).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
